NEW INFO | Discussing the latest information from various media and various fields
Agriculture: Empowering Sustainable Food Systems
Agriculture: Empowering Sustainable Food Systems
Agriculture plays a crucial role in sustainable food systems, ensuring the availability, accessibility, and affordability of nutritious food while preserving the environment for future generations.

Transforming Food Systems | Diets and climate, how FBDG can help - Source www.genevaenvironmentnetwork.org
| Conventional Agriculture | Sustainable Agriculture |
|---|---|
| Focuses on maximizing yields | Prioritizes environmental conservation and social equity |
| Relies heavily on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides | Promotes organic farming, crop rotation, and integrated pest management |
| Leads to soil degradation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions | Enhances soil health, protects water resources, and mitigates climate change |
- Climate-Smart Practices: Minimizing environmental impact, enhancing resilience.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Preserving ecosystem diversity, safeguarding natural resources.
- Nutrition Security: Ensuring access to nutrient-rich diets, combating malnutrition.
- Technological Advancements: Precision farming, data analytics, empowering efficiency.
- Policy Frameworks: Encouraging sustainable practices, fostering innovation and collaboration.
- Empowered Farmers: Investing in education, training, and resources for thriving livelihoods.
FAQ
Agriculture: Empowering Sustainable Food Systems is a comprehensive guidebook that provides invaluable insights into the complex challenges faced by today's food systems. It offers evidence-based solutions and practical strategies to promote sustainable agricultural practices, ensuring food security and environmental preservation. This FAQ section addresses common concerns and misconceptions surrounding agriculture's role in shaping sustainable food systems.

The Importance Of Sustainable Food Systems: Adoption And Examples - Source www.sustainablejungle.com
Question 1: What are the primary challenges facing agriculture today?
Answer: Agriculture grapples with a myriad of challenges, including climate change, population growth, and resource scarcity. Climate change poses significant threats to crop yields and livestock production, while increasing population pressures exacerbate demands on finite land and water resources. Moreover, environmental concerns related to agricultural practices, such as deforestation and water pollution, have become pressing issues.
Question 2: How can agriculture contribute to sustainable development?
Answer: Sustainable agriculture practices promote environmental conservation, economic viability, and social equity. By optimizing resource use, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and enhancing biodiversity, agriculture can contribute to mitigating climate change and protecting ecosystems. Furthermore, sustainable agriculture supports rural livelihoods and improves resilience against future challenges.
Question 3: What role do technology and innovation play in sustainable agriculture?
Answer: Technology and innovation are crucial enablers of sustainable agriculture. Precision farming techniques, data analytics, and biotechnology have the potential to optimize crop production, reduce environmental impact, and enhance resource efficiency. Digital technologies can also improve market access for smallholder farmers and empower rural communities.
Question 4: How can consumers support sustainable agriculture?
Answer: Consumers have a significant role to play in promoting sustainable agriculture by making informed choices about the food they consume. Supporting local producers, choosing organic and environmentally friendly products, and reducing food waste are effective ways to promote sustainable practices. Additionally, advocating for policies that encourage sustainable agriculture and food systems is essential.
Question 5: What are the key indicators of sustainable agriculture?
Answer: Indicators of sustainable agriculture include soil health, water conservation, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration. Sustainable agricultural systems aim to maintain soil fertility, conserve water resources, enhance biodiversity, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Monitoring these indicators helps evaluate the progress and effectiveness of sustainable agriculture practices.
Question 6: How can we ensure that agriculture remains accessible and affordable for all?
Answer: Ensuring accessibility and affordability of agricultural products requires a multifaceted approach. Government policies, such as subsidies and infrastructure development, can support smallholder farmers and reduce production costs. Promoting local food networks, investing in rural infrastructure, and reducing market barriers are also vital. Additionally, consumer awareness about the environmental and social benefits of sustainable agriculture can create demand for ethically and sustainably produced food.
The FAQs provided in this section shed light on the complexities of agriculture and its critical role in shaping sustainable food systems. By addressing common concerns and providing evidence-based information, we hope to foster a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities in agriculture. It is through collective efforts and a commitment to sustainability that we can create a resilient and equitable global food system for present and future generations.
Transition to the next article section: Exploring the latest advancements and innovations in sustainable agriculture.
Tips
Agriculture plays a vital role in ensuring sustainable food systems and fostering global food security. By adopting innovative practices, we can enhance agricultural productivity while preserving the environment and ensuring the well-being of future generations. Here are a few essential tips to consider:
Tip 1: Embrace Sustainable Land Management
Sustainable land management involves practices that preserve soil health, protect watersheds, and mitigate climate change. Techniques such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and conservation tillage contribute to soil fertility and reduce erosion, safeguarding the integrity of agricultural lands for future use.
Tip 2: Promote Integrated Pest Management
Integrated pest management (IPM) emphasizes the use of non-chemical methods to control pests and diseases. By employing a holistic approach that combines biological control, cultural practices, and targeted pesticide use, IPM minimizes environmental impact while maintaining agricultural productivity.
Tip 3: Enhance Water Efficiency
Water scarcity poses a significant challenge to sustainable agriculture. Employing water-efficient irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting, can conserve water resources and reduce agricultural runoff, minimizing the risk of water pollution.
Tip 4: Promote Agroforestry
Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into agricultural systems, offering numerous benefits. Agroforestry practices can improve soil health, enhance biodiversity, reduce erosion, and provide additional income sources for farmers. By incorporating trees into agricultural landscapes, we can foster a more resilient and sustainable ecosystem.
Tip 5: Invest in Research and Development
Ongoing research and development are crucial for advancing sustainable agriculture. By investing in innovative technologies, such as precision agriculture and climate-resilient crop varieties, we can improve agricultural efficiency and mitigate the effects of climate change. Collaboration between academia, industry, and farmers is essential to drive innovation and progress.
These tips provide a foundation for transforming agriculture into a more sustainable and resilient sector. Embracing sustainable practices not only ensures food security and environmental preservation but also contributes to the well-being of present and future generations.
For more insights into sustainable agriculture, explore Agriculture: Empowering Sustainable Food Systems
Agriculture: Empowering Sustainable Food Systems
In the quest for sustainable nourishment, agriculture plays a critical role. Empowering sustainable food systems involves multifaceted facets that shape a resilient and equitable future for generations.
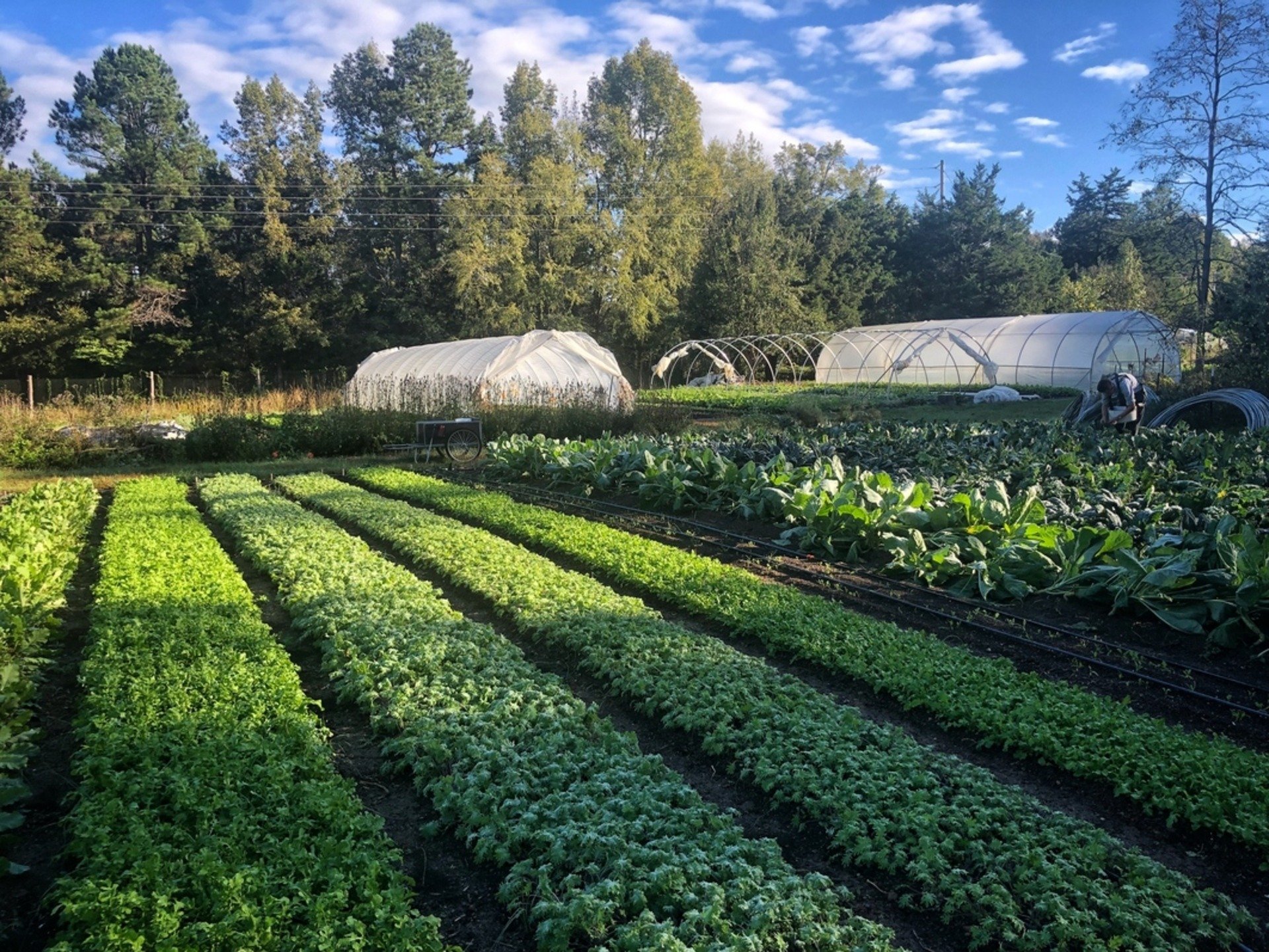

Sustainable Agriculture | FoodPrint - Source foodprint.org
These aspects are interconnected, each contributing to the sustainability of food systems. Climate-smart practices reduce emissions and enhance resilience, protecting biodiversity. Conservation efforts preserve ecosystems that support agriculture and safeguard against environmental degradation. Nutrition security ensures health and well-being, while technological advancements drive efficiency and productivity. Policy frameworks provide incentives for sustainable practices and support farmer livelihoods. Ultimately, empowering farmers with knowledge and skills is essential for long-term sustainability, ensuring that agriculture continues to nourish communities while safeguarding the planet.

Ecosystem-based Adaptation in Agriculture: A Path to Climate-resilient - Source www.unep.org
Agriculture: Empowering Sustainable Food Systems
Agriculture is crucial for sustaining food systems. Sustainable agriculture practices, like crop rotation and integrated pest management, maintain soil health, reduce chemical inputs, and enhance biodiversity. This ensures long-term food security and environmental conservation. For instance, in Kenya, the adoption of sustainable farming techniques has increased crop yields, improved soil fertility, and reduced water pollution.
Empowering Youth with Systems Thinking - KnowledgeWorks - Source knowledgeworks.org
Moreover, agriculture plays a vital role in mitigating climate change. Sustainable practices like agroforestry and conservation tillage sequester carbon and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. For example, in Brazil, the implementation of sustainable agriculture practices has significantly reduced deforestation rates and helped preserve the Amazon rainforest.
Empowering sustainable food systems through agriculture requires collaboration among governments, farmers, researchers, and consumers. Policies that promote sustainable agriculture, investments in research and education, and consumer awareness campaigns are essential. By fostering a shared understanding of the importance of sustainable food systems, we can ensure a resilient and equitable future for generations to come.
Table: Key Insights
| Insight | Example |
|---|---|
| Sustainable agriculture practices enhance food security and environmental conservation. | Crop rotation and integrated pest management in Kenya |
| Agriculture mitigates climate change. | Agroforestry and conservation tillage in Brazil |
| Empowering sustainable food systems requires collaboration and awareness. | Government policies, research, and consumer campaigns |
Conclusion
Agriculture is the foundation of sustainable food systems, providing sustenance and maintaining environmental health. By embracing sustainable agricultural practices, we can ensure food security, mitigate climate change, and preserve our planet for future generations.
The journey towards sustainable food systems requires a collective effort, where governments, farmers, and consumers work together to create a resilient and equitable future. By valuing and investing in sustainable agriculture, we can create a world where everyone has access to healthy and nutritious food, while protecting our planet and ensuring its sustainability.